In my last post about QEMU I showed how easy it was to emulate the Raspberry Pi in Windows. If you are just getting started with the Pi, that is the way to go. Personally, I prefer to use Arch Linux over Debian. There is nothing wrong with Raspbian, I am just used to how Arch Linux works. But, emulating Arch Linux under QEMU is not that simple. To start, not everything can be found in one easy download package. But, I worked through the problems and here are the instructions:
- To start,you will need a working QEMU working Rasbian to modify the Arch Linux img file. Follow the instructions in this post to get Raspbian running.
- Next, download QEMU 1.6 from QEMU FOR WINDOWS (52MB). Extract in a different location from the Rasbian install.
- Download the latest Linux kernel for QEMU from http://xecdesign.com/downloads/linux-qemu/kernel-qemu NOTE: http://xecdesign.com/qemu-emulating-raspberry-pi-the-easy-way/ has some great information about QEMU and the Raspberry Pi
- Download the latest Arch image from http://archlinuxarm.org/platforms/armv6/raspberry-pi
- Before we boot the Arch image we are going to make a few changes to the img file. One, it needs to be bigger and have a swap partition and two, the way the Arch image specifies the boot partition does not work with QEMU. We need to modify the /etc/fstab to make it work.
- Add 2 GB of space to the fake SD card with the following command (in Windows)
qemu-img <Arch img filename> resize +2G - Next, we will add the Arch img as a second drive in Rasbian. Add the following to the BAT file that starts the Rasbian QEMU session
-hdb ArchLinuxARM-20##.##-rpi.img
Add the correct date code for you file. That addition puts the Arch img on /dev/sdb when you start Rasbian. - Start Rasbian. Watch the messages to see that the sdb partitions are now available. Don’t worry if the message go by too quickly, the next step can also check.
- Now create the swap partition. Login and use
sudo fdisk /dev/sdband create a linux swap partition. Detailed instructions are here. The next step shows how to edit the fstab to make the swap used at boot. - Next, we will mount the Arch partition and edit the fstab. Do the following:
sudo mkdir /mnt/arch
sudo mount /dev/sdb5 /mnt/arch
sudo nano /mnt/arch/etc/fstab - In fstab, change the /boot line from /dev/mmcblk0 to /dev/sda1
- Add the following as the list line to activate swap on boot
/dev/sda3 none swap defaults 0 0 - Save fstab, exit nano and umount /mnt/arch.
- Halt Rasbian and move the Arch img file to the QEMU 1.6 install directory
- Arch can be started with the following command
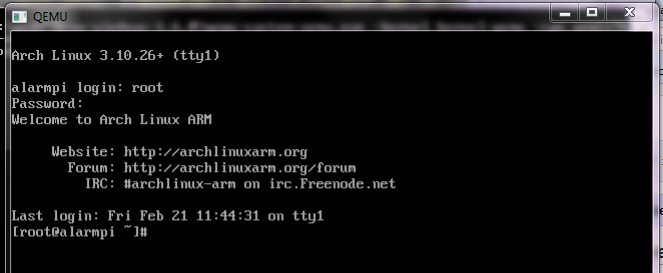
qemu-system-armw.exe -kernel kernel-qemu -cpu arm1176 -m 256 -M versatilepb -no-reboot -serial stdio -append "root=/dev/sda5 panic=1 rootfstype=ext4 rw" -hda ArchLinuxARM-2014.02-rpi.img - All should start and you can log in with username root and password root
- Check your swap with
free -m
You’re done. You new have a QEMU system emulating Arch Linux. Update Arc with pacman to get all of the latest goodness.